What is COPD – What are symptoms for COPD
Symptoms for COPD have been mentioned in detail below.
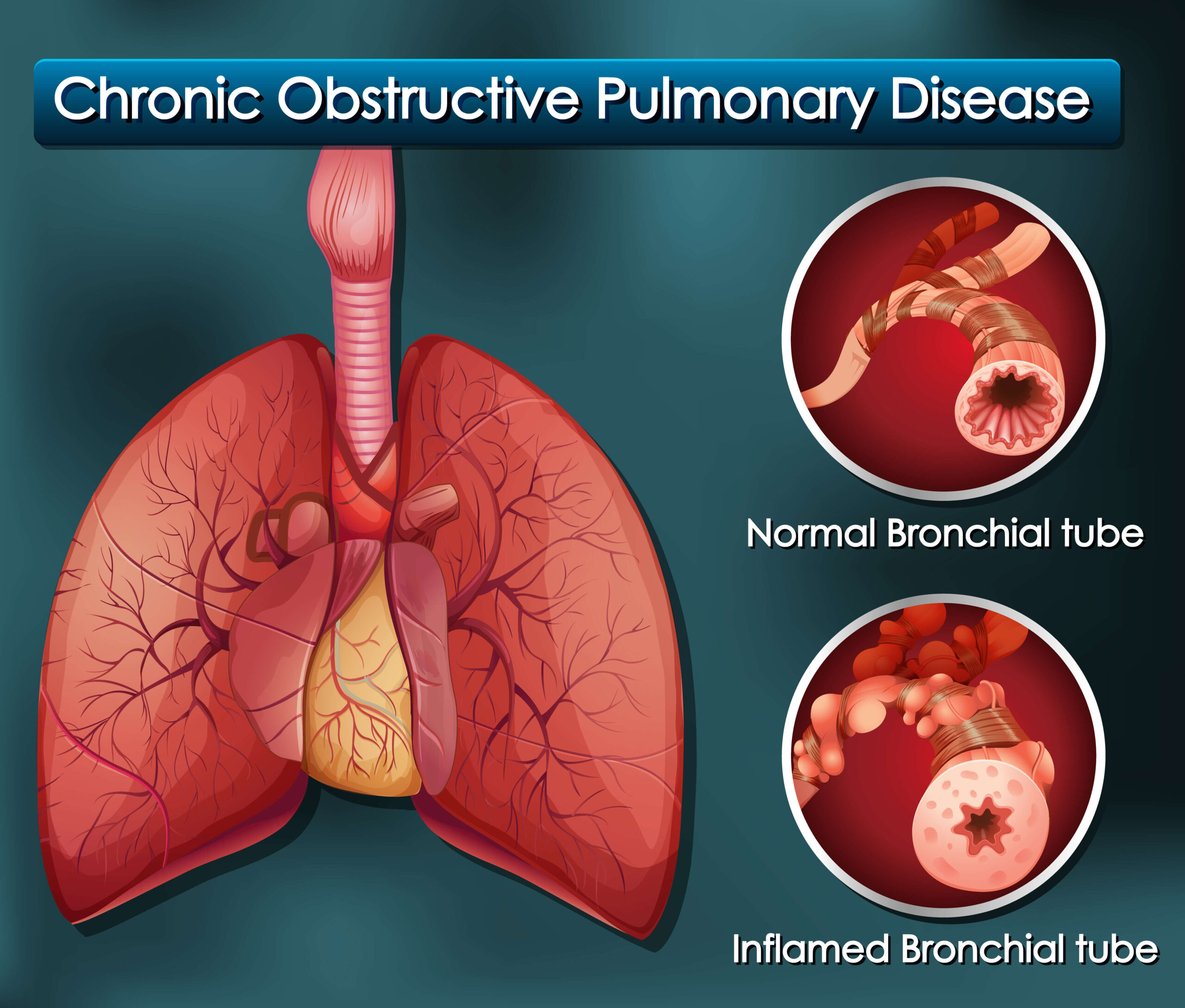
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive and long-term inflammatory lung condition characterized by a persistent cough and shortness of breath.
COPD is an umbrella term given to a group of progressive lung diseases that make it harder to breathe air out of the lungs. These diseases include Chronic bronchitis, in which the bronchi (large air passages) are inflamed and scarred, and Emphysema, in which the alveoli (tiny air sacs) are damaged.
What are the causes of COPD
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD because the toxic compounds in cigarettes can injure the lining of the lungs and airways. Additionally, smoking harms cilia, preventing them from performing their function of clearing mucus and other trapped particles from the airways. Quitting smoking can help stop the deterioration of COPD.
90% of COPD cases are related to smoking tobacco.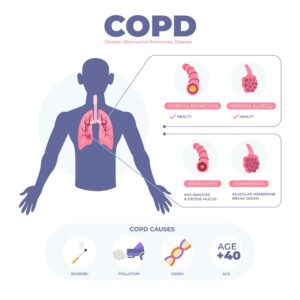
Other inhaled irritants that can lead to COPD include other people’s smoking (Passive Smoking), air pollution, dust, and fumes at work.
Rarely, a genetic disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency may contribute to the onset of COPD.
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AAT) is a rare hereditary condition that can cause emphysema. An enzyme called alpha-1 antitrypsin aids in shielding your lungs from the harmful effects of inflammation. AAT insufficiency causes insufficient production of alpha-1 antitrypsin which increases your risk of lung injury when exposed to irritating elements like smoke and dust. (1)
Risk factors for COPD
- Smoking: The biggest risk factor is smoking.
- Other Irritants: Passive smoking (being exposed to other people’s smoking) increases the risk of COPD. Additionally, the risk of COPD is increased by prolonged exposure to air pollution, dust, and fumes at work.
- Age: The majority of COPD sufferers start experiencing symptoms at a minimum of 40 years of age.
- Genetics: Includes Alpha-1 antitrypsin insufficiency. Additionally, if a smoker has a family history of COPD, their risk of developing the disease increases.
What are Symptoms for COPD
Many people do not notice COPD symptoms until the condition has progressed significantly. Often people believe that they are “simply getting older” when they feel out of breath or less capable of carrying out their daily duties. Breathlessness is a significant sign of lung illness. (2)
Breathing becomes more difficult with COPD. Initially, the symptoms could be slight, starting with sporadic coughing and shortness of breath. The symptoms may worsen and become more frequent as the condition worsens, making breathing more challenging. There could be excessive sputum production, wheezing, and chest discomfort. Acute exacerbations, or flare-ups of severe symptoms, can occur in certain COPD sufferers. 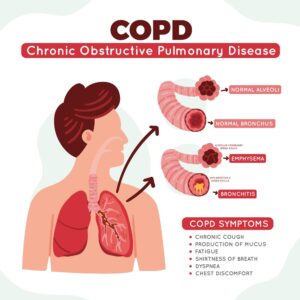
Initial signs and symptoms
A person may falsely assume they have just a cold if they experience the mild initial symptoms of COPD. Early signs and symptoms include infrequent shortness of breath, especially after exertion, a minor but persistent cough, and frequent throat clearing, especially in the morning.
Perhaps you begin to make small adjustments, like avoiding the stairs and missing workouts.
Aggravating signs and symptoms
The severity of symptoms can increase over time, making them more difficult to ignore. As the lungs deteriorate, you may feel the following symptoms: shortness of breath after even climbing a flight of stairs; wheezing; chest tightness; loss of energy; a persistent cough with or without mucus which needs to remove from your lungs on a daily basis; Recurrent colds, flu, or other respiratory infections
Advanced Stage Symptoms
Fatigue, swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, and weight loss are further symptoms of COPD in its advanced stages.
If you smoke or are constantly around people who smoke, your symptoms are probably going to be more severe.
Remember: Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen because this will waste crucial treatment time. Effective treatment of COPD depends on early identification.
How to test yourself for COPD
a. Spirometry:
Spirometry is a basic test that determines how well your lungs function. Spirometry can identify COPD even before symptoms appear. The test results may also be used by your doctor to assess the severity of your COPD and establish treatment objectives.
b. Other tests:
-
- Chest X-rays can help to point out heart failure, emphysema, and other lung conditions.
- An arterial blood gas test determines the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- Using numerous X-rays, a CT scan can produce a thorough image of your lungs.
Treatment for COPD
Since there is no cure, the aim of treatment is to reduce your symptoms and decelerate the disease. Additionally, your doctor will work to enhance your general quality of life and prevent or cure any issues.
Quitting smoking is one of the finest things you can do to prevent the progression of your COPD.
Medical treatment
-
- Bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles surrounding your airways. This facilitates better breathing by widening your airways.
- Corticosteroids: These medicines ease inflammation in the airways.
- Antibiotics: to treat viral and bacterial lung infections.
- Roflumilast (Daliresp): This medicine inhibits the PDE4 enzyme. In those whose COPD is connected to chronic bronchitis; it prevents flare-ups.
- Vaccinations against the flu or pneumonia: Your risk of respiratory diseases like COVID-19 is reduced by these immunizations.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
This program helps people with chronic respiratory issues to improve their health. To support you in maintaining the best level of health and activity, it could include an exercise program; training in disease management; and nutritional and psychological counselling.
Oxygen Therapy
You may require this to alleviate shortness of breath, protect your organs, and improve your overall quality of life.
Surgery
Surgery is reserved for patients with severe COPD or when all other therapies have failed. Your doctor may recommend:
-
- Bullectomy: Removes bullae, which are huge air gaps formed when air sacs collapse.
- Lung volume reduction surgery: Removes damaged upper lung tissue, which can improve breathing.
- Lung transplantation: Substitutes a healthy lung for a damaged one
Non-invasive treatments
Zephyr Endobronchial Valve (Zephyr Valve), is used to treat severe emphysema-related breathing problems. Emphysema patients who use the Zephyr Valve have exhibited improvements in lung function, exercise tolerance, and quality of life. Endobronchial valves (EBV) are one-way valves that directly inspire air toward healthy lungs and away from lungs with disease or dysfunction. (3)
Must Read >>
- What is the Health Benefits of Ginger.
- What are Generic Medicine: Myths and Facts.
- Exercise During Pregnancy: Do’s and Don’ts
- Breast Cancer Awareness: Its Importance and Benefits
- What are the benefits of coconut water
- Weight loss exercise from home
- Exercises for frozen shoulder at home
- Why is water important to us
- How to stop hair fall in men